The healthcare industry has been flailing as of late due to the documented inability of organizations to meet the needs of the increased number of patients while also keeping quality of care at high levels.
The adoption rate of digital transformation, digital platforms and new technologies is going fast, but unfortunately, it is not fast enough to service the plethora of patients that require healthcare.
Augmented Reality (AR) has the ability to be easily integrated in a myriad of ways within healthcare organizations, providing organizations with the means to gather a mountain of data that can be used to increase quality of care exponentially. AR can also be integrated into surgeries and medical training, thereby digitally transforming an entire organization and industry from the inside out.
Augmented reality technology
AR technology is used to add value to real world scenarios via the use of overlaying and displaying real-time digital information and media, such as videos and 3D models to your intended area of view. By 2025, the AR and Virtual Reality (VR) space in the healthcare industry is predicted to reach $5.1 billion, allowing it to leapfrog the engineering ($4.7 billion), real estate ($2.6 billion), and retail ($1.6 billion) industries.
Tim Cook, CEO of Apple, explains that “AR is going to take a while, because there are some really hard technology challenges there. But it will happen, it will happen in a big way, and we will wonder when it does, how we ever lived without it. Like, we wonder how we lived without our phone today.” Coming from the CEO of one of the largest technology companies in the world, this quote seems like an omen of a possible future that rings true for a myriad of industries.
Healthcare industry struggles
Ever since the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) was passed by the U.S. Congress on August 21, 1996, it has led to the digital evolution of documentation within the healthcare industry. HIPAA was meant to simplify the administration of health insurance and allow for more continuity of health insurance coverage, but the rate of adoption for the technology to bridge the gap into the future was slower than expected. Healthcare practitioners were so used to hand scribbling patient notes and prescriptions on paper parcels that the transition to digitization was met with many roadblocks.
Health IT Policy and Interoperability Influencer, Brian Ahier, elaborates on this by explaining that “technology cannot simply just be implemented within a place of work. Work flow adjustments need to be enforced and when considering the technology side of things, there needs to be successful integration and interoperability between systems.” This is incredibly true for the healthcare industry which manages its compliance efforts using legacy systems that often don’t contain enough information to adequately support administrative staff at the point-of-purchase. AR can enable healthcare organizations to save millions of dollars by maximizing efficiencies which has a direct positive effect on the bottom line.
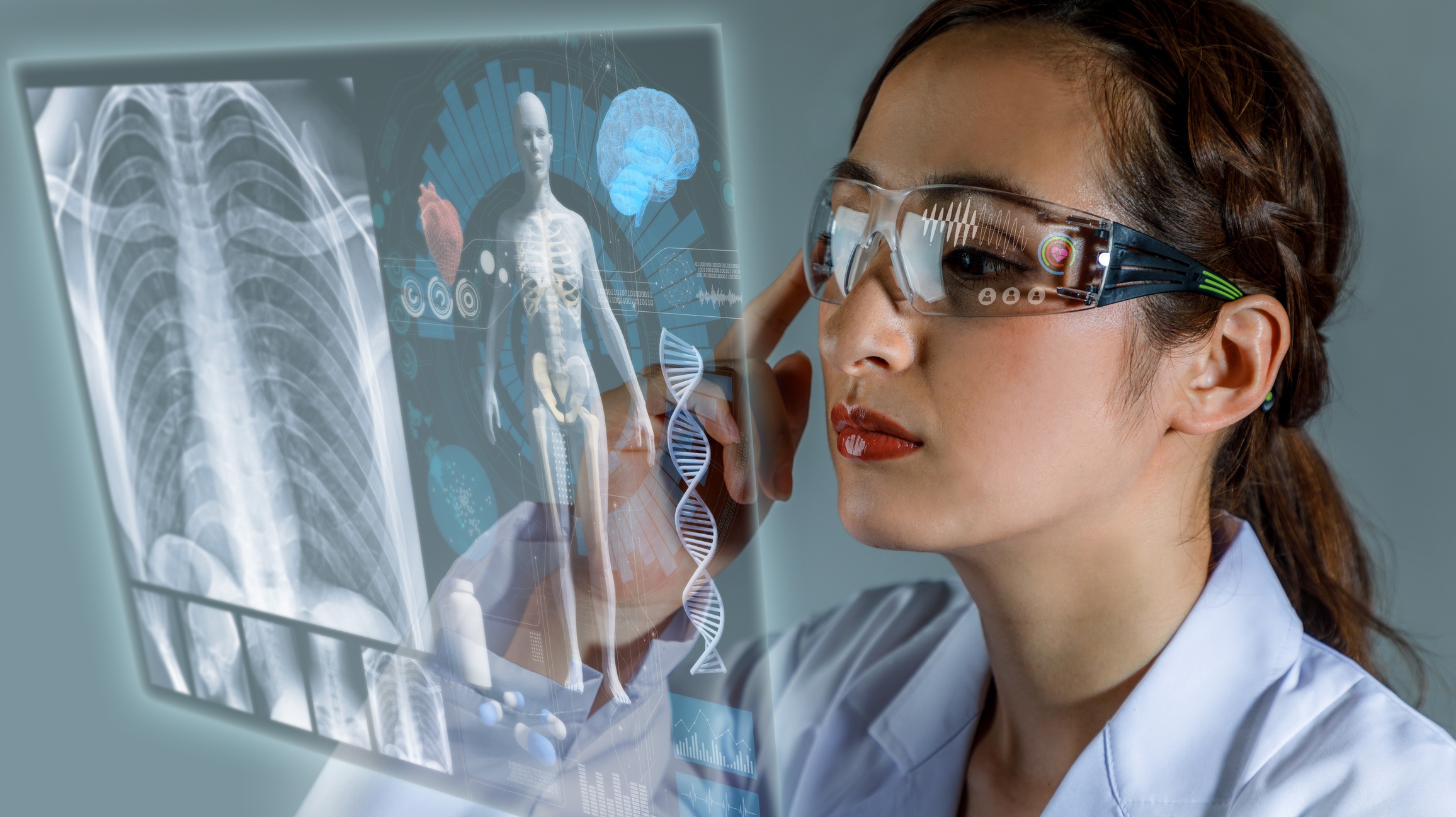

How AR can help
AR has the ability to redefine how providers deliver care to patients with chronic conditions in a variety of ways. AR technology allows for medical knowledge, skills and expertise to be shared remotely in real- time, ensuring that the recipient (patient and/or staff) can receive timely information from the doctor or administrative staff. Medical staff can complete tasks more accurately and efficiently, allowing them to service more patients with a higher level of quality care. AR can also be used to improve patient education on pharmaceutical products by visualizing complex instructions via 4D holograms.
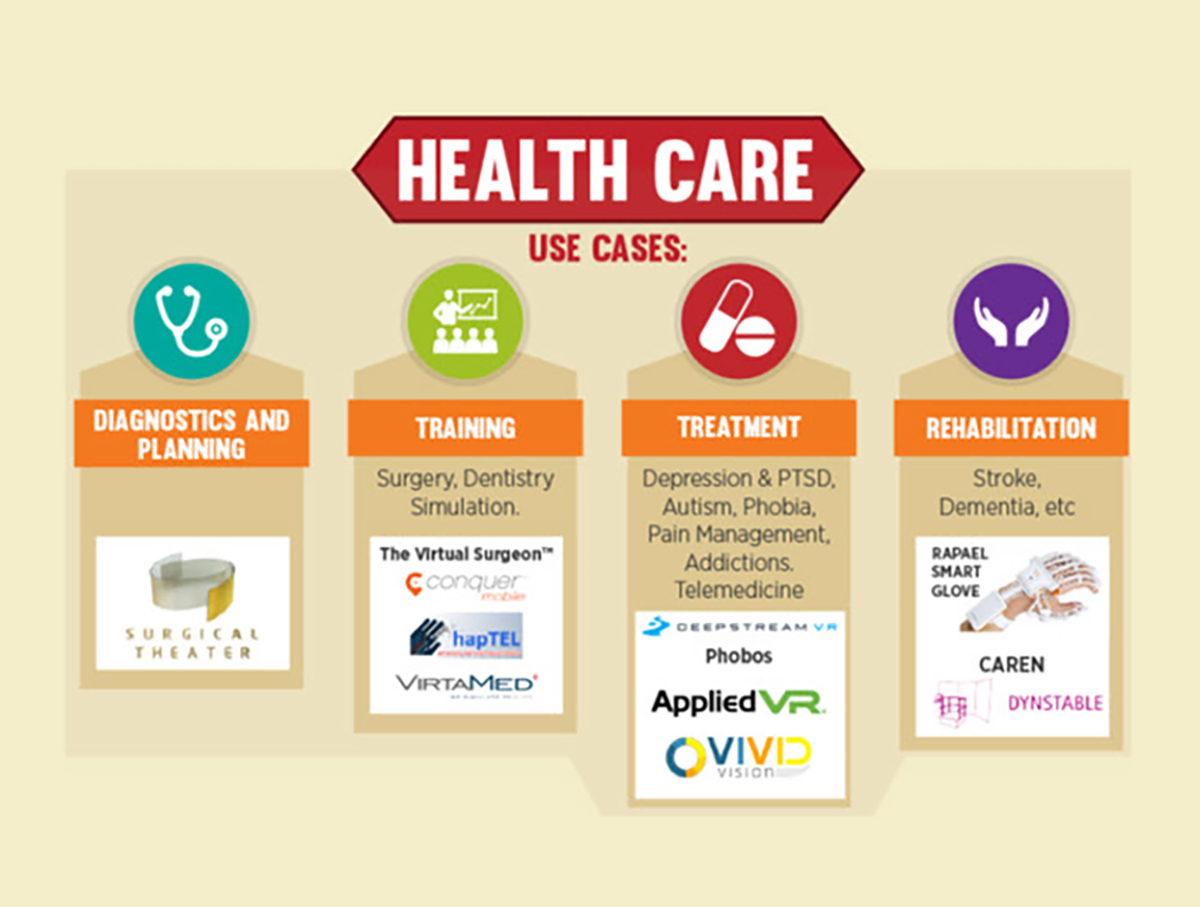
AR apps can be used to better illustrate the impact of particular diseases and give way to seamless patient/doctor interactions in an enhanced and simulated environment that can gather patient data that can be used to develop customized care plans. Upon leaving the hospital, patients can then use AR technology to continue with their treatments at home, thereby lowering the rate of hospital re- admissions for the same treatment.
Surgeries
There were 48 million surgical inpatient procedures performed in the U.S. in 2009. The following year, that number hit 51.4 million and has been climbing ever since. There are also more than one million spinal surgeries performed in the U.S. alone. This increase in demand for surgical procedures calls for doctors to become more efficient and effectively with their maneuvers while also maintaining the same high quality of care.
This daunting task is made possible through the integration of AR hologram images which gives surgeons a better perspective of a patient’s body makeup and allowing them to digitally plan out the procedure accordingly. This increased effectiveness gives way to a decrease in prevalence of medical malpractice and errors during surgeries, ultimately allowing doctor-patient relationships to improve. The impact of using AR in surgery could also mean the improvement of outcomes which could possibly mean the reduction of costs down the road.
Medical training
One of AR’s biggest advantages is being able to clearly demonstrate and visualize intricate concepts for the next generation of medical staff. Key Board Member of the American College of Healthcare Trustees, Irma Rastegayeva, explains that “Augmented Reality empowers surgeons and other health professionals to explore human body in great detail and enhance medical education.” AR applications offer medical staff of all skill levels and disciplines the ability to visualize and interact with accurate representations of the human body instead of relying on printed information for guidance.
Using AR to train employees or students at any level of education provides an immersive, multi-sensory experience that results in greater depth of training and speed to mastery. No longer will real human cadavers need to be rolled out to give students an in-depth look at the human anatomy. Instead, AR will be used to project a holographic cadaver with simulated internal organs and information pertaining to every part of the body that the student wishes to the interact with. Many who have experienced these holographic mannequins feel that they offer a much more lifelike and responsive simulation that is close enough to the real thing for them to adapt their training into real life scenarios easily.
Closing thoughts
Although the healthcare industry has hit several speed bumps in their quest to get up to speed with HIPAA, AR has been waiting in the wings to innovate the present to bring the industry up to speed in a big way. AR has the ability to transform this industry for the better via offering significant improvements to the quality of treatment that patients receive from their healthcare provider inside and outside the hospital.
New and innovative instances of AR are rolled out in a variety of facets within the healthcare industry, patients and practitioners alike are seeing first-hand that the technology plays a significant role in helping us live longer and lead safer, healthier, more productive lives. Our client, Kaiser Permanent is innovating again, after the KP Thrive campaign that skyrockets their brand relevance, KP has the project to open a medical school in 2020 with focus on teaching students how to use technology to deliver high quality in new and collaborative ways.
We strategize, design, and build exceptional digital experiences that solve complex brand challenges.
Propane, Creative Agency
1153 Mission Street
San Francisco, CA - 94103
415 550 8692